简介
Record是从Java 14开始引入的新特性,Record提供了一种简洁高效的方式来创建不可变类。
引入
使用Java进行开发的时候,程序员经常会创建一些不可变类专门用于承载数据(也就是MVC模型中的model),这些类可能涉及大量的样板代码,包括:
- 大量的
private、final、public关键字
- 每个字段的getter
- 重写
equals()、hashCode()、toString()方法
例如以下代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
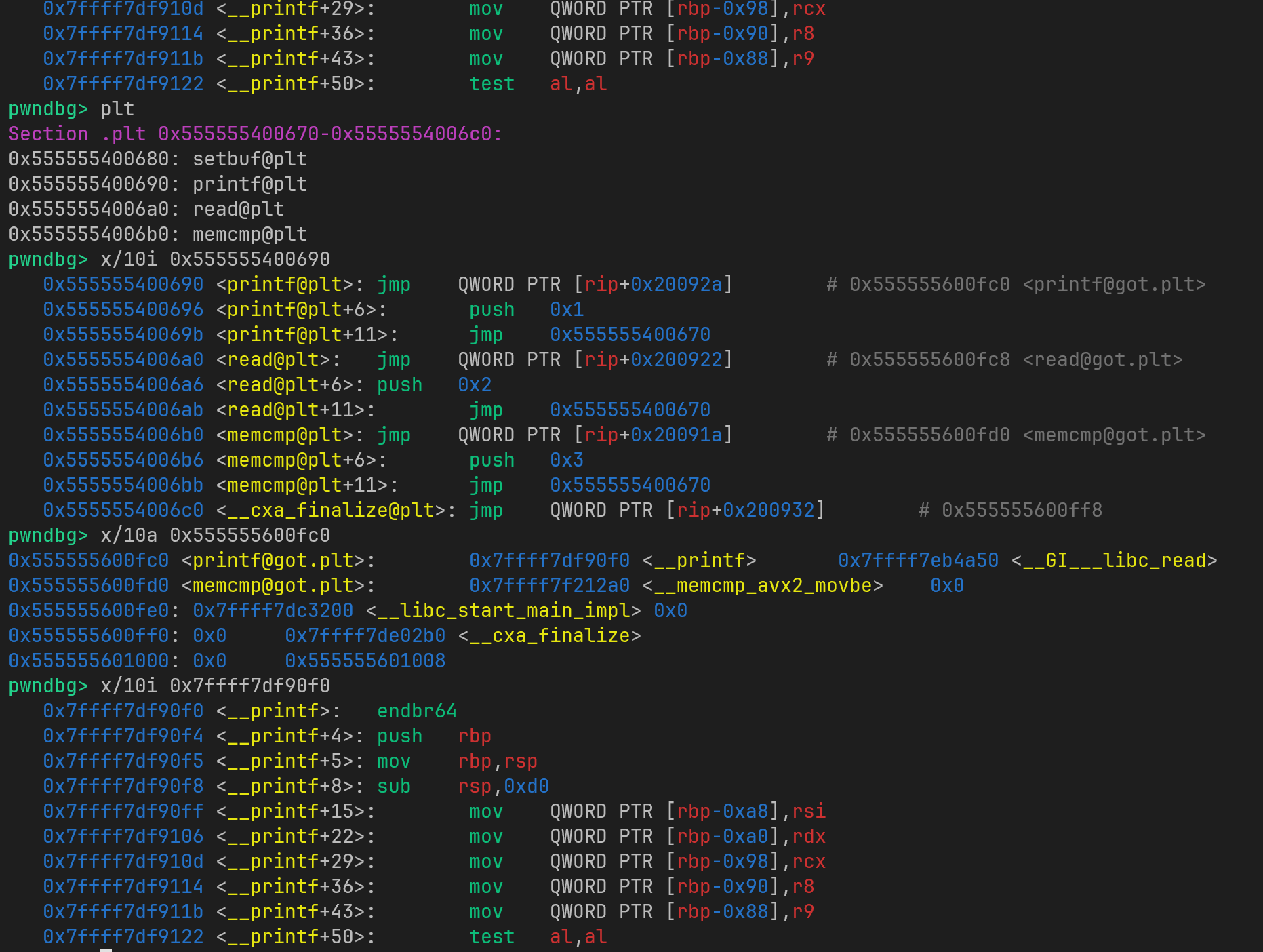
| package example;
import java.util.Objects;
public final class Person {
private final Long id;
private final String name;
private final Integer age;
public Person(Long id, String name, Integer age) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public Long getId() {
return id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true;
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;
Person user = (Person) o;
return Objects.equals(id, user.id) &&
Objects.equals(name, user.name) &&
Objects.equals(age, user.age);
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(id, name, age);
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person[" +
"id=" + id +
", name=" + name + '\'' +
", age='" + age + '\'' +
']';
}
}
|
使用record类就可以简化为
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| package example;
public record Person (
Long id,
String name,
Integer age
) {}
|
record类的特性
- 自动生成带有所有参数的构造方法
- 自动生成每一个字段的getter方法,使用同名的
public方法。
- 没有setter方法,这是因为记录类是不可变的
- 自动重写
toString()方法,具体逻辑参考第一种Person类代码
- 自动重写
hashCode()方法
- 自动重写
equals()方法,判定两个对象相等当且仅当二者类型相同,且每个字段都相等
- 每一个属性都是
final,不可修改
final类,不可被继承
定义
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
| package example;
public record Student(
Long id,
String name,
Double englishScore,
Double mathScore
)
{
public static int count = 0;
public Student {
count++;
}
public Double score() {
return englishScore * 0.4 + mathScore * 0.6;
}
}
|
解释一下上面的构造函数,实际上这段代码
1
2
3
| public Student {
count++;
}
|
和以下代码是等价的
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| public Student(Long id, String name, Double englishScore, Double mathScore) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.englishScore = englishScore;
this.mathScore = mathScore;
count++;
}
|
是不是很方便!
使用
运行以下代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| package example;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student student = new Student(1L, "cyrus28214", 60.0, 70.0);
Student student2 = new Student(1L, "cyrus28214", 60.0, 70.0);
System.out.println(Student.count);
System.out.println(student.equals(student2));
System.out.println(student.hashCode());
System.out.println(student.toString());
System.out.println(student.name());
System.out.println(student.score());
}
}
|
将输出
1
2
3
4
5
6
| 2
true
1360019156
Student[id=1, name=cyrus28214, englishScore=60.0, mathScore=70.0]
cyrus28214
66.0
|
作用
record可以极大简化不可变类的代码,而不可变类在JPA中非常常见,所以可以利用record来写JPA:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| import jakarta.persistence.Entity;
import jakarta.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import jakarta.persistence.GenerationType;
import jakarta.persistence.Id;
import jakarta.persistence.Table;
@Entity
@Table(name = "users")
public record User (
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
Long id,
String username,
String passwordHash
) {}
|
与传统的写法来说,可以少写很多代码,拯救你的手指。
更多支持的功能
record类还支持以下功能,和正常的类的使用方法是一致的:
- 使用泛型
- 实现接口
- 添加注解
- 序列化和反序列化
- 作为局部类(Local Class)使用
- 嵌套定义
- 支持
instanceof
参考
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/643804004
https://docs.oracle.com/en/java/javase/17/language/records.html#GUID-6699E26F-4A9B-4393-A08B-1E47D4B2D263